日前出版的权威杂志《公共科学图书馆—综合》(Plos ONE)发表了来自温州医学院药学院的一项研究成果。研究人员通过探索成纤维细胞生长因子21(FGF21)与慢性肾病(CKD)发病之间的关系,揭示了FGF21在慢性肾病发病中的重要意义。
领导这一研究的是温州医学院教授、长江学者李校堃。李校堃是温州医学院药学院院长,国家基因药物工程研究中心首席科学家。他专注于重组蛋白药物的基础及创新药物研究,积累了丰富的生物药物理论研究和开发经验。他领导的研究团队在国内外首次成功开发3个FGF系列基因工程一类新药,目前已在上海、广东等地投产。
研究人员通过观察不同CKD阶段的肾病患者FGF21血清水平变化状况及其与肾功能之间的关系,发现血清肌酐的浓度与FGF21的表达呈正相关,而肾小球滤过率与FGF21呈负相关趋势,因此在一定程度上可以利用外周血FGF21水平的变化来反映肾病患者肾功能的严重程度,为早期诊断肾病提供检测指标。
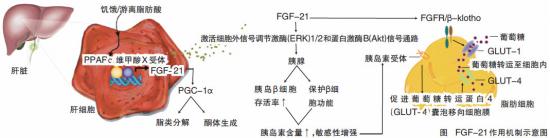
FGF21是成纤维细胞生长因子家族的新成员,是一种特异性作用于肝脏、胰岛和脂肪组织的新型代谢调控因子。FGF21具有降低机体血糖血脂、改善胰岛素抵抗、保护胰岛β细胞等多种糖脂代谢调控的功能,因此,其在Ⅱ型糖尿病、肥胖、动脉粥样硬化、脂肪肝等多种代谢综合征的临床应用方面极具潜力。据了解,李校堃领衔的科研团队将在“十二五”期间重点对FGF家族新成员FGF21进行新药的研究开发。
此外,在国家新药创制重大专项的支持下,该研究团队还开展了FGF21的PEG化学修饰研究,采用mPEG-丁醛修饰剂对FGF21的N末端进行特异性修饰,修饰产率稳定在40%以上,纯度达到95%。PEG-FGF21不仅很好地保留了FGF21的生物学活性,而且稳定性和体内半衰期都显著提高,在动物试验中证实了FGF21经过PEG修饰后,其降糖降脂等效应显著延长,为FGF21的新药开发提供了重要的实验基础,有关该项研究的报告也发表在近期出版的Plos ONE杂志上。
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Circulating FGF21 Levels Are Progressively Increased from the Early to End Stages of Chronic Kidney Diseases and Are Associated with Renal Function in Chinese
Background
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a hepatic hormone involved in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. This study aims to test the hypothesis that elevated FGF21 concentrations are associated with the change of renal function and the presence of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in the different stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression.
Methodology/Principal Findings
240 subjects including 200 CKD patients (146 outpatients and 54 long-term hemodialytic patients) and 40 healthy control subjects were recruited. All CKD subjects underwent echocardiograms to assess left ventricular mass index. Plasma FGF21 levels and other clinical and biochemical parameters in all subjects were obtained based on standard clinical examination methods. Plasma FGF21 levels were significantly increased with the development of CKD from early- and end-stage (P<0.001 for trend), and significantly higher in CKD subjects than those in healthy subjects (P<0.001). Plasma FGF21 levels in CKD patients with LVH were higher than those in patients without LVH (P = 0.001). Furthermore, plasma FGF21 level correlated positively with creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), β2 microglobulin, systolic pressure, adiponectin, phosphate, proteinuria, CRP and triglyceride, but negatively with creatinine clearance rate (CCR), estimated glomerular filtrate rate (eGFR), HDL-c, LDL-c, albumin and LVH after adjusting for BMI, gender, age and the presence of diabetes mellitus. Multiple stepwise regression analyses indicated that FGF21 was independently associated with BUN, Phosphate, LVMI and β2 microglobulin (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
Plasma FGF21 levels are significantly increased with the development of early- to end-stage CKD and are independently associated with renal function and adverse lipid profiles in Chinese population. Understanding whether increased FGF21 is associated with myocardial hypertrophy in CKD requires further study.